
Killer whale OCX043 encountered with three other whales 175km west of Bandon, Oregon, September 9, 2021. This whale was sighted previously 300 km offshore of Monterey Bay, California on January 23
Based on available evidence, the researchers posit in a new study published in Aquatic Mammals that the 49 orcas could belong to a subpopulation of transient killer whales or a unique oceanic population found in waters off the coast of California and Oregon.
“The open ocean is the largest habitat on our planet and observations of killer whales in the high seas are rare,” said first author Josh McInnes, a masters student in the UBC Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries (IOF).”In this case, we’re beginning to get a sense of killer whale movements in the open ocean and how their ecology and behaviour differs from populations inhabiting coastal areas.”
Three ecotypes of killer whale live along the coasts of California and Oregon: ‘residents’, ‘transients’, and ‘offshores’.
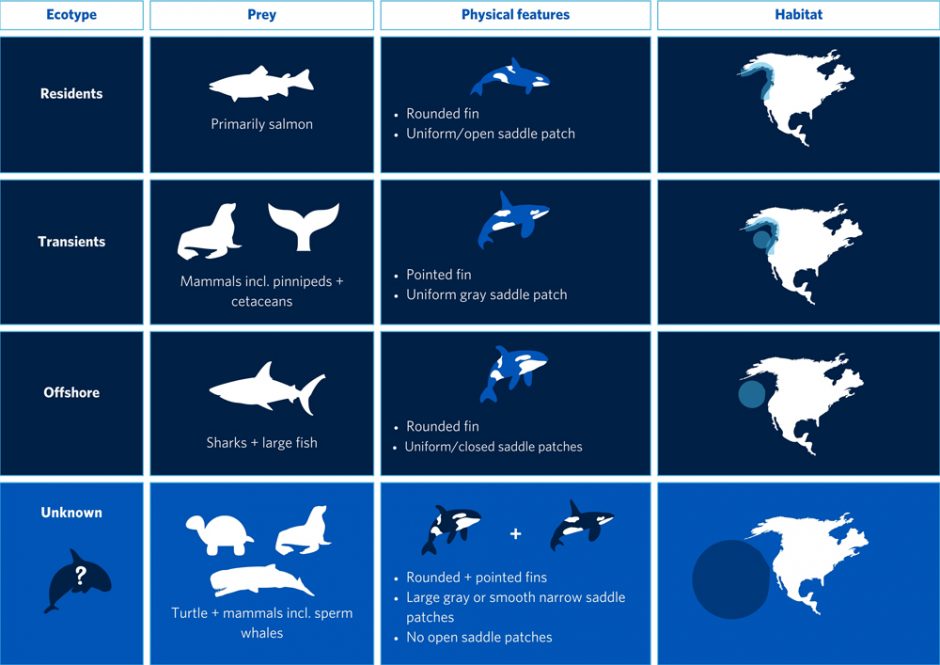
An infographic showing the differences between the three orca ecotypes that live along the coasts of California and Oregon and the potential unique population. Credit UBC
The unknown orcas have been spotted before but the new paper contains a weight of evidence gathered from nine encounters with 49 animals from 1997 to 2021, enough to form a solid hypothesis, the researchers said.
“It’s pretty unique to find a new population. It takes a long time to gather photos and observations to recognize that there’s something different about these killer whales,” said co-author Dr. Andrew Trites, IOF professor.

An adult female or subadult male oceanic killer whale OCX040 attacking a Risso’s dolphin in Monterey Bay, California August 25, 2021. Photo credit Slater Thomas Moo
Shark scars provide vital clue
A key clue to the new population’s presumed habitat range lies in cookiecutter shark bite scars observed on almost all of the orcas. This parasitic shark lives in the open ocean, meaning the new population primarily inhabit deep waters far from land.
The orcas also feature physical differences from the three main ecotypes, including in their dorsal fins and saddle patches—the grey or white patches by the fin. “While the sizes and shapes of the dorsal fins and saddle patches are similar to transient and offshore ecotypes, the shape of their fins varied, from pointed like transients to rounded like offshore killer whales,” said McInnes. “Their saddle patch patterns also differed, with some having large uniformly gray saddle patches and others having smooth narrow saddle patches similar to those seen in killer whales in tropical regions.”
Along with marine mammal stock assessment surveys, fishermen and passengers on an open-ocean birding expedition and whale-watching tour also provided observations of the unidentified killer whales, said Dr. Trites. Spotting the new population has become something of a hobby among fishermen, some of whom have bought cameras for their trips specifically to snap an encounter, the researchers said.
The researchers hope to document more sightings and gather more information, including acoustic data about the orcas’ calls and genetic information from DNA samples to further investigate how these killer whales may differ, or not, from already documented populations.
Tags: Andrew Trites, IOF students, Josh McInnes, killer whales, Marine Mammal Research Unit, marine mammals, orca, Pacific Ocean, Research, whales